Tag: Natural ventilation
[Case study] Fordia – Energy efficiency and energy savings opportunities in the industry
[Case study] Fordia – Energy efficiency and energy savings opportunities in the industry Like many players in today’s society, industry stakeholders are taking concrete action to reduce energy consumption and reduce their impact on climate change. Fordia is focusing on drastically reducing its global carbon emissions and has launched a global Energy Efficiency program on all of its operations combined
[Expertise] Thermal comfort: how to face more frequent heat waves? – Part 2
In our Part 1 article, we have introduced Thermal comfort principle and some essential passive design ideas to optimize buildings for frequent heatwaves. In this article, we continue to introduce other simple yet essential ways to avoid thermal discomfort in a building. Optimization of the envelope Thermal insulation, compactness and glazing rates should be optimized to minimize heating and cooling
[Expertise] Thermal comfort: how to face more frequent heat waves? – Part 1
In the current context of ever more numerous and intense heat waves, the notion of thermal comfort in buildings is more relevant than ever. In June, France experienced temperatures 10°C to 15°C above seasonal norms. July and August also brought their share of heat waves! Beyond national climate objectives and the reduction of its impacts, the construction sector must also
[Expertise] Energy modeling: a powerful tool for sustainable buildings
Energy modeling is a whole-building simulation process that engineers, architects, and researchers use to model the energy consumption of heating, cooling, ventilation, lighting, electronic equipment, and process loads. The simulation can give hourly time step results or even sub-hourly time step results (for example, 15 minutes) which makes it possible to carry out a detailed analysis of the thermal behavior
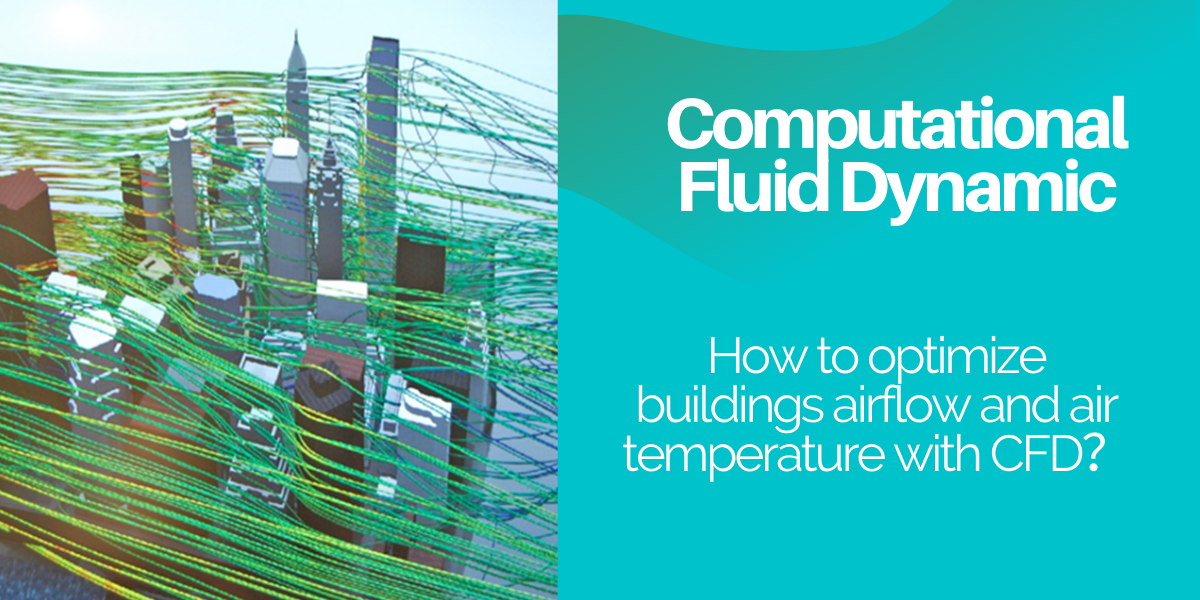
[Expertise] How to optimize buildings airflow and air temperature with Computational Fluid Dynamic (CFD)
Computational Fluid Dynamic (CFD) is a tool used to analyze fluid flows and temperature. In the case of building and environmental engineering, it can be used for internal spaces (large spaces such as warehouses, exhibition spaces or workshops) or external spaces (districts, neighborhoods or cities). In internal space, CFD is used to calculate thermal comfort via the calculation of airspeed, air temperature, “age” of air







Recent Comments