The building envelope is the physical barrier between the indoor and outdoor environment of a building. It includes the walls, roof, windows, doors and other elements that separate the interior space from the exterior climate. The building envelope plays a crucial role in determining the energy performance, thermal comfort and indoor air quality of a building. In this article, we will explain the key concept of the building envelope, how it works and why it is important for energy efficiency.
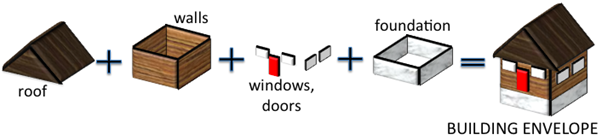
How does building envelope work?
The building envelope consists of two main parts: the opaque envelope and the transparent envelope. The opaque envelope refers to the solid elements of the building, such as the walls, roof and floor, that provide structural support and insulation. The transparent envelope refers to the openings in the building, such as the windows, doors and skylights, that allow natural light and ventilation to enter the indoor space.
The building envelope acts as a filter that regulates the heat, air and moisture transfer between the indoor and outdoor environment. Depending on the climate and season, the building envelope can either retain or release heat, block or admit solar radiation, prevent or allow air infiltration and control or facilitate moisture diffusion. The building envelope also influences the acoustic comfort and fire safety of a building.
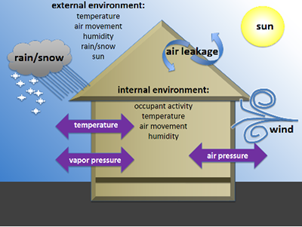
It works by performing three main functions:
– Support: The building envelope provides structural stability and strength to the building. It resists and transfers loads from wind, snow, earthquakes, and other forces.
– Control: The building envelope controls the flow of matter and energy between the indoor and outdoor environments. It regulates temperature, humidity, air quality, ventilation, lighting, acoustics, and fire safety.
– Finish: The building envelope gives the building its appearance and aesthetics. It reflects the architectural style, design intent, and cultural values of the building.
Why is the Building Envelope Important for Energy Efficiency?
The building envelope‘s impact on energy consumption should not be underestimated: in some countries with similar climates, it can take twice as much energy to heat the same floor area depending on the quality of the envelope. Moreover, the building envelope also affects the comfort, indoor environmental quality and safety of the occupants, as well as the embodied carbon impact of the building materials.
The building envelope is one of the most important factors that affect the energy efficiency of a building. Compared to other solutions, the selection of envelope structure and materials is particularly important given the long lifetime of buildings and the cost of construction. By controlling the flow of matter and energy between the conditioned and unconditioned environment, the building envelope plays a crucial role in improving energy efficiency.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, about 40% of the energy consumption in buildings is attributed to heating, cooling and lighting. A well-designed and constructed building envelope can significantly reduce the energy demand for these services by improving the thermal performance and daylighting of a building.
A high-performance building envelope can:
– Reduce the thermal needs of buildings, making them more energy-efficient and reducing energy consumption.
– By properly insulating the building envelope, huge amounts of energy can be saved. Applying thermal insulation on the outer surfaces of building envelopes can also significantly reduce annual cooling loads and peak demands.
– Building envelope technologies account for approximately 30% of the primary energy consumed in residential and commercial buildings, so it plays a key role in determining levels of comfort, natural lighting, ventilation, and how much energy is required to heat and cool a building.

By reducing the energy demand for heating, cooling and lighting, a high-performance building envelope can lower the operating costs, greenhouse gas emissions and environmental impact of a building. It can also improve the comfort, health and productivity of the occupants. It is key to apply bioclimatic design principles to adapt the characteristics of the envelope to the local climate characteristics.
How to Design and Construct a High-Performance Building Envelope?
The design and construction of a high-performance building envelope requires an integrated approach that considers the climate, site, function and aesthetics of a building. There is no one-size-fits-all solution for creating an optimal building envelope. However, some general principles and best practices can be followed to achieve a better energy performance:
– Conduct a site analysis to determine the climatic conditions, solar access, wind patterns and other environmental factors that affect the building envelope.
– Perform an energy analysis to estimate the heating, cooling and lighting loads of a building and identify the potential energy savings from different envelope options.
– Select appropriate materials and systems for the opaque and transparent envelope with high thermal resistance, low thermal bridging, low emissivity, high solar transmittance or reflectance and low air leakage.
– Apply passive design strategies such as orientation, shading, thermal mass, natural ventilation and daylighting to reduce or eliminate the need for mechanical systems.
– Implement quality control measures such as testing, inspection and commissioning to ensure that the building envelope meets or exceeds the design specifications.
Improving the energy efficiency of the building envelope is not only a matter of technology but also of policy and regulation. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), more than 110 countries lacked mandatory building energy codes in 2022, meaning that around 2.4 billion square meters of floor space were built without meeting any energy-related performance requirements. To achieve net-zero emissions by 2050, the IEA recommends that all countries establish zero-carbon-ready building energy codes for both new and existing buildings by 2030 at the latest. This means that buildings should be highly energy-efficient and resilient, and either use renewable energy directly or rely on a source of energy supply that can be fully decarbonized.
Conclusion
The building envelope is a key component of a sustainable and energy-efficient building. It acts as a physical barrier that regulates the heat, air and moisture transfer between the indoor and outdoor environment of a building. By designing and constructing a high-performance building envelope that suits the climate, site and function of a building, it is possible to reduce the energy demand for heating, cooling and lighting services. This can result in lower operating costs, greenhouse gas emissions and environmental impact of a building. It can also improve the comfort, health and productivity of the occupants.
TERAO as a Building Sustainability Engineering Consultancy can provide you with support in balancing between natural daylighting, comfort, and energy efficiency. TERAO has been a pioneer of the Bioclimatic design approach in tropical and sub-tropical climates; an expert in passive design strategies, focusing on maximizing the building envelope performance.
Explore more:
- How to optimize buildings with CFD
- Energy modeling: a powerful tool for sustainable buildings
- Thermal comfort improvement for factories – the right approach
We hope you find this expertise article insightful and valuable. If you have any questions or would like to learn more, please don’t hesitate to contact our Business Development Director Gaspard at glemoinescelles@teraoasia.com.




Leave A Comment