Carbon reduction methodology for new construction projects is a systematic approach to reducing greenhouse gas emissions from the design, construction, operation and maintenance of buildings. It involves assessing the carbon footprint of the project from design to operation, identifying opportunities to reduce emissions through design choices, materials selection, energy efficiency, renewable energy sources and waste management, and compensating for the remaining emissions through carbon offsetting schemes.

Why Carbon Reduction Matters for Construction
The building sector is one of the major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for about 38% of the global energy-related CO2 emissions in 2019, according to the International Energy Agency. Additionally, this sector consumes a large amount of natural resources, such as water, land, and materials, and generates a lot of waste and pollution.
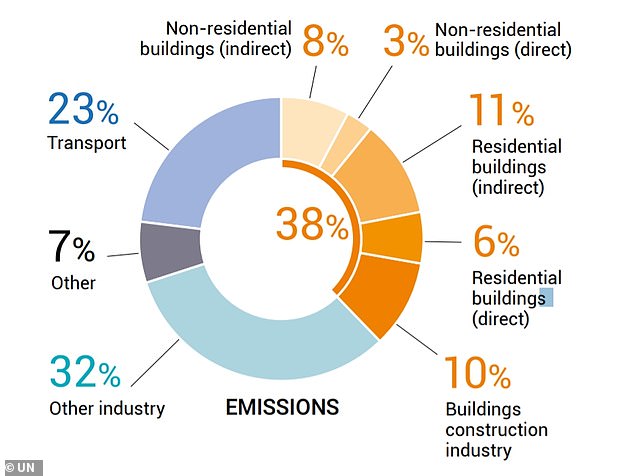
More specifically, the construction sector is responsible for approximately 36% of the total energy consumption and 39% of the carbon dioxide emissions worldwide. The demand for new buildings and infrastructure is expected to increase in the coming years, especially in developing countries, which will further exacerbate the environmental impact of this sector.
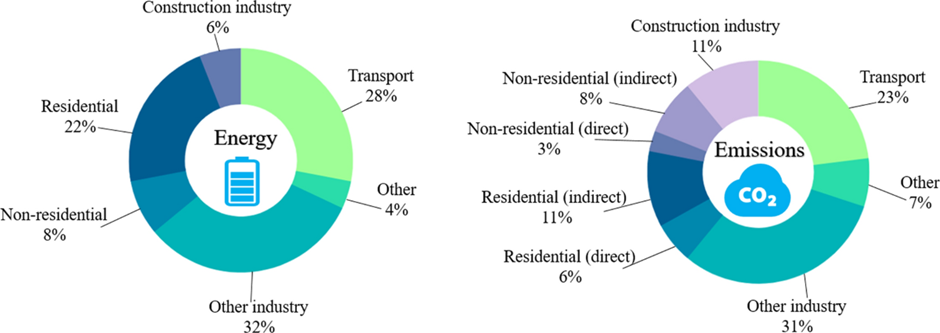
Therefore, it is important to reduce the carbon footprint of new construction projects, which means lowering the amount of CO2 and other greenhouse gases that are emitted during the life cycle of a building, from design to demolition. This can help mitigate climate change, conserve natural resources, improve air quality, and enhance the resilience and performance of buildings.
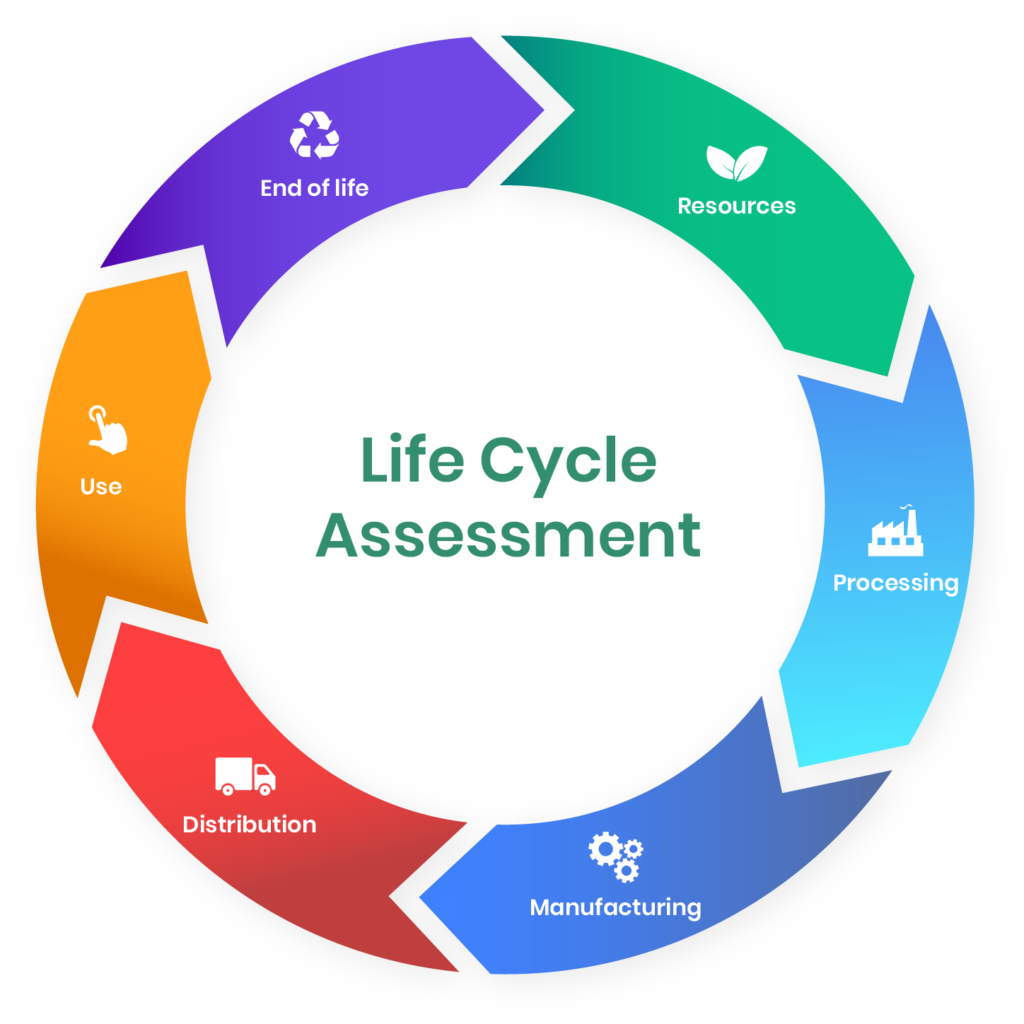
The carbon reduction methodology for new construction projects is based on three main concepts: life cycle assessment (LCA), carbon budget, and carbon offsetting. LCA is a tool that quantifies the environmental impacts of a product or service throughout its life cycle, from raw material extraction to disposal. Carbon budget is the amount of CO2 emissions that can be emitted without exceeding a certain threshold of global warming. Carbon offsetting is the process of compensating for one’s own emissions by investing in projects that reduce or avoid emissions elsewhere.
The methodology consists of four main steps:
1. Define the project scope and boundaries. It defines the functional unit, the system boundaries, the reference scenario and the data sources for the project. The functional unit is a measure of the performance or function of the project, such as the floor area, the number of occupants or the service life. The system boundaries define what processes and activities are included or excluded from the analysis, such as materials production, transportation, construction, operation, maintenance, demolition and disposal. The reference scenario is a hypothetical alternative that represents the conventional or baseline practice for the project type and location. The data sources are the sources of information and data that are used to quantify the carbon impacts of the project, such as databases, literature, standards or measurements.
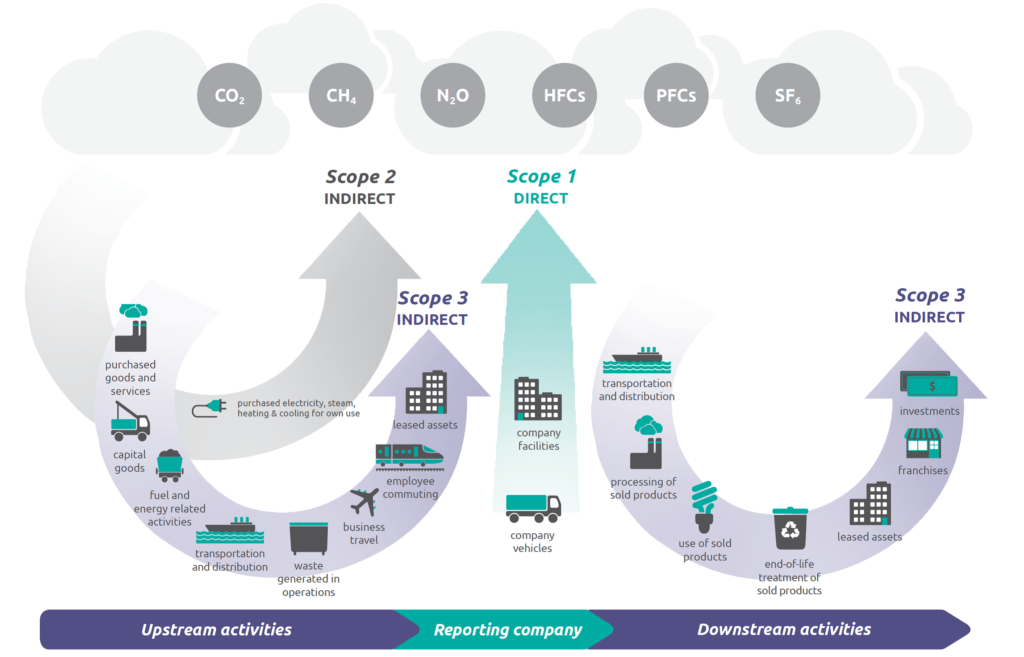
2. Calculate the project’s carbon footprint. This step involves quantifying the carbon emissions and removals associated with each process and activity within the system boundaries, using life cycle assessment (LCA) methods and tools. LCA is a systematic approach to assessing the environmental impacts of a product or service throughout its life cycle. The carbon footprint is expressed as the total amount of CO2 equivalent (CO2e) emissions and removals over the project’s life cycle. The carbon footprint can be further disaggregated by life cycle stage, process, material or component to identify the main sources and drivers of carbon impacts.
3. Identify and evaluate carbon reduction opportunities. This step involves identifying and assessing potential measures and strategies to reduce the carbon footprint of the project, using circular economy principles and carbon pricing tools. The circular economy is a concept that aims to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency by designing products and systems that are durable, reusable, repairable, recyclable and regenerative. Carbon pricing is a tool that assigns a monetary value to the carbon impacts of a product or service, reflecting its social and environmental costs and benefits. Carbon pricing can be applied in different ways, such as carbon taxes, emissions trading schemes or internal carbon fees. By applying circular economy principles and carbon pricing tools, project owners, designers, contractors and stakeholders can compare different options and scenarios based on their carbon performance and economic viability.

4. Implement and monitor the carbon reduction plan. This step involves implementing the selected measures and strategies to reduce the carbon footprint of the project and monitoring their effectiveness and outcomes over time. This step requires setting clear goals and targets, allocating roles and responsibilities, establishing indicators and metrics, collecting data and information, reporting results and feedback, and updating and revising the plan as needed. This step also involves communicating and engaging with relevant stakeholders to ensure their awareness, involvement and support for the carbon reduction plan.
By following this carbon reduction methodology for new construction projects, project owners, designers, contractors and stakeholders can achieve significant benefits for themselves and for society at large, such as:
– Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change
– Saving costs and enhancing profitability
– Improving resource efficiency and reducing waste
– Enhancing innovation and competitiveness
– Increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty
– Demonstrating leadership and responsibility
– Creating positive social and environmental impacts
In conclusion, carbon reduction methodology for new construction projects is a comprehensive and effective way to minimize greenhouse gas emissions from buildings. It involves conducting a life cycle assessment, setting a carbon budget, implementing low-carbon design strategies, and considering carbon offsetting options. It can also bring multiple benefits to building owners, developers, occupants, and society at large.
TERAO is pushing the way to control and reduce the carbon emissions of new construction projects. If you want to learn more about the approach or another method, feel free to contact us at glemoinescelles@teraoasia.com for further information. We would be pleased to assist you.
Explore more:
[Expertise] Carbon reduction vs Carbon offset
[Case Study] Forvia Fengcheng Mega Plant _LEED v4 Gold
Carbon Footprint Methodology – How to assess your asset environmental impact?



2 Comments
Keep this going please, great job!
Thanks in favor of sharing such a nice thought, article is good, thats why i
have read it completely