Since 2008 up to December 2017, over 10,636 projects (over 1 billion square meters) have been certified under China Green Building Label in China, including Green Building Design Label (GBDL-Design phase) and Green Building Label (GBL-Operation Phase); 3401 projects have been assessed in 2017. The following green building map of China can show generally the development situation per region, the darker green color represents a more advanced GBDL/GBL development in that area. The regions in gray do not have any green buildings at present.
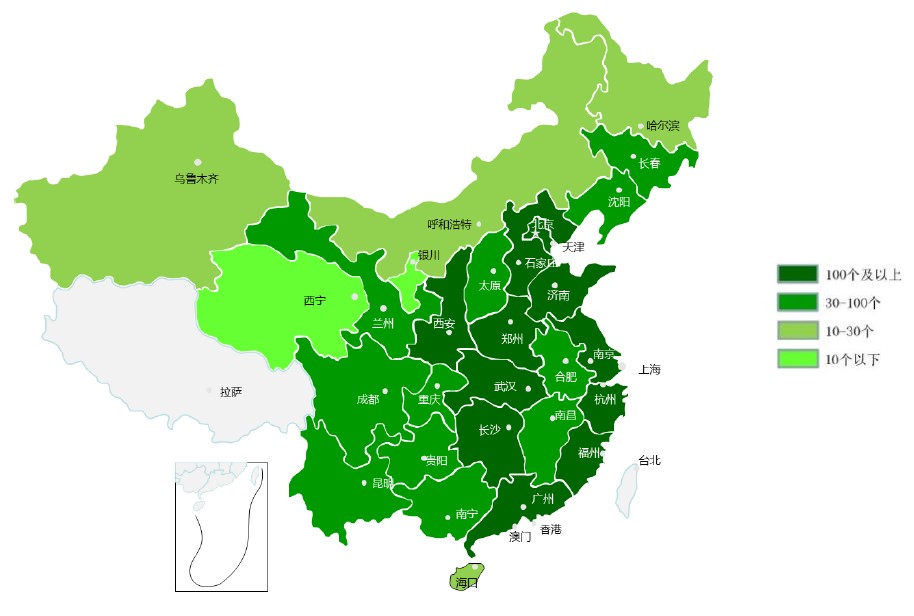
Source: 中国城市科学院就会绿色建筑研究中心 The Green Building Research Center of CSUS
After several rounds of expert consultation, the new version of GBL GB/T 50378-2019 was released in early 2019 and has been implemented since August 1st, 2019. Here is a summary of some major changes between the former versions and this new version.
Change 1: Evaluation is not divided anymore between Design Evaluation (GBDL) and Operation evaluation (GBL) 1 year later, but is now performed at the completion of the construction; evaluation at the end of design stage, when construction drawings are completed is considered as “pre-evaluation” only.
More residential buildings need to be fully fitted to be evaluated (not Core and Shell).
Change 2: A “basic level” has been added and higher points to reach are required to get the 1-star, 2-star or 3-star level.
| GBDL/GBL 2014 | => |
New GBL 2019 |
||
| Basic level: | 40 points | |||
| 1 star | 50-59 points | 1 star | 60-69 points | |
| 2 stars | 60-79 points | 2 stars | 70-84 points | |
| 3 stars | >=80 points | 3 stars | >=85 points | |
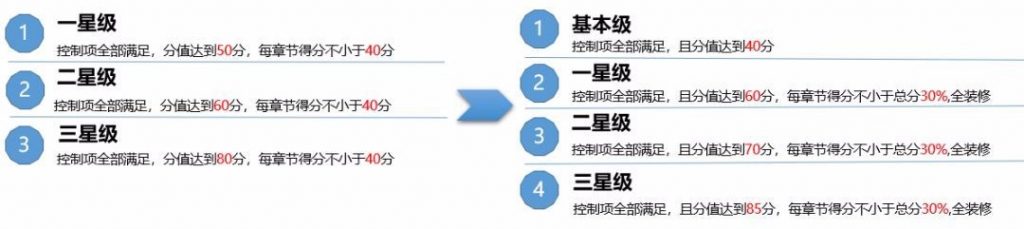
Addition of “Basic level” and additional requirements to reach 1-star, 2-star and 3-star levels; Source: 中国建筑科学研究院有限公司, PKPM及网络
The basic level(基础级)is the level where all «Control items »(控制项) have been fulfilled. They constitute 40 points over the 100 total points that could be obtained.
Besides fulfilling the basic level and their respective points requirements, level 1, 2 and 3 buildings need to fulfill respective mandatory technical requirements on these 6 items:
- Envelope thermal or air conditioning load optimization
- Heat transfer coefficient of external windows of residential projects in severe cold and cold regions
- Water-saving appliances
- Residential building sound insulation
- Indoor air pollutant concentration
- Outer window air tightness
Change 3: “以人为本,强调性能,提高质量”. A more “People-oriented, emphasizing performance and improving quality” version
Any people living in China could note that Health is at the center of the Chinese way of life, so it is no surprise that the WELL standard is working pretty well here (China registered projects are the first and second in ranking before US cities numbers) and that now the new version of GBL focus more on the relationship between people and the environment, and aims at the development of high-quality buildings.
It can be illustrated by the change in the assessment categories which were then 7 utility or resources-oriented categories, and now become 5 people-oriented categories:
- Safety and Durability (100 points),
- Healthy and comfortable (100 points),
- Convenience of Occupation (100 points),
- Resources conservation (200 points),
- Environment liveability (100 points),

The total score is divided by 10 to give the final score of the building.
Change 4: Increase safety and comfort
The first two editions of the Standard did not cover the promotion of physical and mental health in the building. The new standard reflects safety, health and fitness requirements in various chapters, such as building balconies, stairs, floor-to-ceiling windows, etc. fall-prevention measures (anti-slippery floor…), suitable for old age, suitable technical measures, barrier-free facilities, outdoor communication space, fitness conditions, liveable outdoor environment, indoor air quality improvement, water quality requirements, comfortable indoor environment.
Change 5: Increase natural ventilation, natural light
The new version will have higher requirements for natural ventilation (ref. Chapter 5.2.10).
Daylighting simulation requirements are more stringent and now static and dynamic simulation need to be done, whereas static was enough for the previous version.
Change 6: Introduction of the concept of Green Building Materials
The GBDL/GBL strives to improve the quality of buildings, and especially green materials in buildings: the different standards for 28 types of building materials are under draft for now by the China Engineering Construction Association (中国工程建设协会).
If these kinds of materials are used in the project (cf. §7.2.18), they can add up to a total of 12 points in the total of 200 points for Category IV “Resources Conservation”.

Green building Materials label
Change 7: Performance-based indoor air quality evaluation
In relation to materials, indoor air quality would be better evaluated in the new GBL, as a special chapter shows:
5.2.1: Control the indoor pollutant concentration and evaluate the total score by 12 points.
❶ Ammonia, formaldehyde, benzene, total volatile organic compounds, cesium and other pollutants are lower than the current national standard “Indoor air quality standards” GB/T18883 limit by 10%, get 3 points; below by 20%, get 6 points;
❷ Average annual concentration of PM 2.5 in the room is not higher than 25 mg/m3, and the indoor average concentration of PM10 is not higher than 50 mg/m3, which is 6 points.
It means the indoor air quality will have to be monitored to be able to have the right data.
Change 8: BIM technology application evaluation score increased to 15 points (innovation points)
The total score allocated to the usage of BIM increased from 2 points (former version) to 15 points in the new version.
BIM can help to better manage design change and construction management and reduce overall costs due to errors in the transfer of changes.
Crossroads with other international standards
China Green Building Label new version is more aligned with other International Green Building standards, making it easier to assess a building under the China Green Building standard which is recognized in the Chinese market with other international standards recognized by International players.


![[Expertise] How to conduct an energy audit to identify areas of energy waste in business](https://teraoasia.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/Expertise-1-150x150.jpg)

Leave A Comment